
1.1 Purpose of Audits
Operator licence holders must have systems ensuring the safe and legal operation of vehicles. Independent audits help identify compliance issues, and traffic commissioners may require these as proof of compliance to avoid regulatory actions. This guide outlines the requirements for acceptable audits.
1.2 Key Audit Guidelines
Audits should be conducted by independent, qualified personnel. An ISO 9001:2015 certification is a good qualification indicator, though not required. Audits are often done in line with DVSA standards, and operators should verify that an audit provider’s process meets these needs. Generally, audits are conducted in person, but some elements may be reviewed remotely if auditors have access to relevant documentation.
1.2.1 Audit Evidence Requirements
- Preferably, documents should be viewed in hard copy; otherwise, high-quality scanned images are acceptable.
- Publicly accessible data (e.g., vehicle tax and MOT history) should be utilised.
- Login credentials must remain secure and not shared with auditors.
- Remote access can be provided at the operator’s discretion, and video conferencing can be used for remote verification.
- Auditors should confirm the identity of key personnel before interviews and debriefs, which ideally include both a director/partner and the Transport Manager for standard licences.
1.3 Sample Sizes
When checking vehicle and trailer records, the following sample sizes are appropriate:
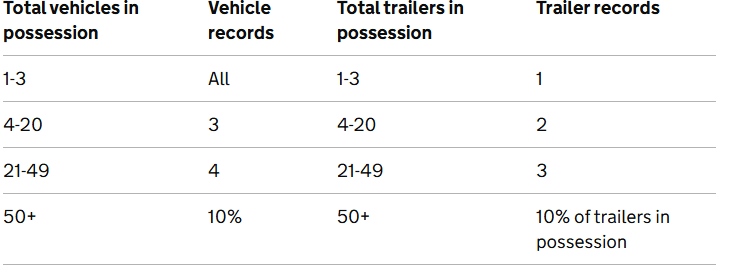
When checking driver records, the following sample sizes are appropriate:

Standard Audit Framework with Autocheck Integration
2.1 Auditor and Audit Scope
Audits should clearly outline the auditor’s qualifications and experience, describing the audit’s approach, evidence review, and individuals involved. For multi-licence holders, audits should specify which licence was reviewed and any operating centres visited.
2.2 Operator Business Profile
The audit should verify key details like licence type and status, number of vehicles, compliance with VOL (Vehicle Operator Licensing) requirements, and employee count. It should also check for industry memberships (e.g., FORS, CLOCS) and review the operator’s key contracts.
Autocheck Advantage: Autocheck helps maintain these records in a centralised system, offering easy access to data on drivers, vehicles, and compliance documents.
2.3 Management Structure and Processes
Audits assess decision-making, driver employment contracts, driver assessments, and bonus schemes, ensuring they align with compliance standards. Checks are made to see if drivers are hired on a PAYE basis or through agencies, with appropriate employment contracts.
Autocheck’s Role: Autocheck assists in maintaining driver information, making management oversight seamless.
2.4 Company Repute
The audit examines any past convictions or pending actions related to directors, owners, or managers.
2.5 Operating Centre and Transport Manager Compliance
Audits confirm the operator’s right to operate from their site, as well as the transport manager’s status and involvement in daily operations.
2.6 Driver Management
Audits look into recruitment, induction, ongoing training, and policies for safety checks, drink and drug testing, and medical requirements. Driver qualification and licensing are closely monitored.
Autocheck’s Role: Autocheck provides customisable inspection sheets, including driver checks and compliance monitoring.
2.7 Driver Hours, WTD, and Routing Compliance
Audits assess compliance with driver hours and Working Time Directive (WTD) policies, analysing tachograph data, route planning, and safe navigation (e.g., avoiding restricted areas). Systems for tracking driver cards and compliance are reviewed.
2.8 Vehicle and Trailer Specifications
Audits verify vehicle allocation, insurance, and whether vehicles are suitable for their intended jobs.
Autocheck’s Role: Autocheck includes unlimited customisable DVSA compliant inspection sheets for daily driver checks, HGV MOT check, 6-8 weekly inspections, roller brake tester (RBT), plus more, helping operators meet compliance needs without added costs.
2.9 Maintenance Standards
The audit reviews maintenance scheduling, inspection records, calibration certifications, and adherence to MOT and PMI requirements. Auditors check VOR (Vehicle Off Road) records, brake tests, and defect reports.
Autocheck’s Role: Autocheck simplifies maintenance scheduling, document storage, and defect reporting with inspection sheets and storage options, ensuring all records are easily accessible and compliant.
2.10 Dangerous Goods and PSV Compliance (if applicable)
Audits check dangerous goods safety protocols, vehicle tests, and driver certifications, as well as PSV (Public Service Vehicle) compliance requirements.
Autocheck Overview
Autocheck is a comprehensive, fixed-monthly-fee workshop and inspection system designed to simplify compliance for operators. With no per-user or per-vehicle fees, Autocheck provides unlimited customisable DVSA compliant inspection sheets from daily driver checks to 6-8 weekly inspections, RBTs, and more. This system centralises compliance documentation, enabling operators to efficiently track and meet DVSA standards across all vehicles and personnel.
Interested in seeing how Autocheck can work for your business?
Book a call or schedule a demo to explore the system in detail. Or, if you’d like a deeper dive into Autocheck’s features, fill out our form to receive the Autocheck brochure and see how it will streamline your operations and compliance.
Click Here For The Full DVSA Article



